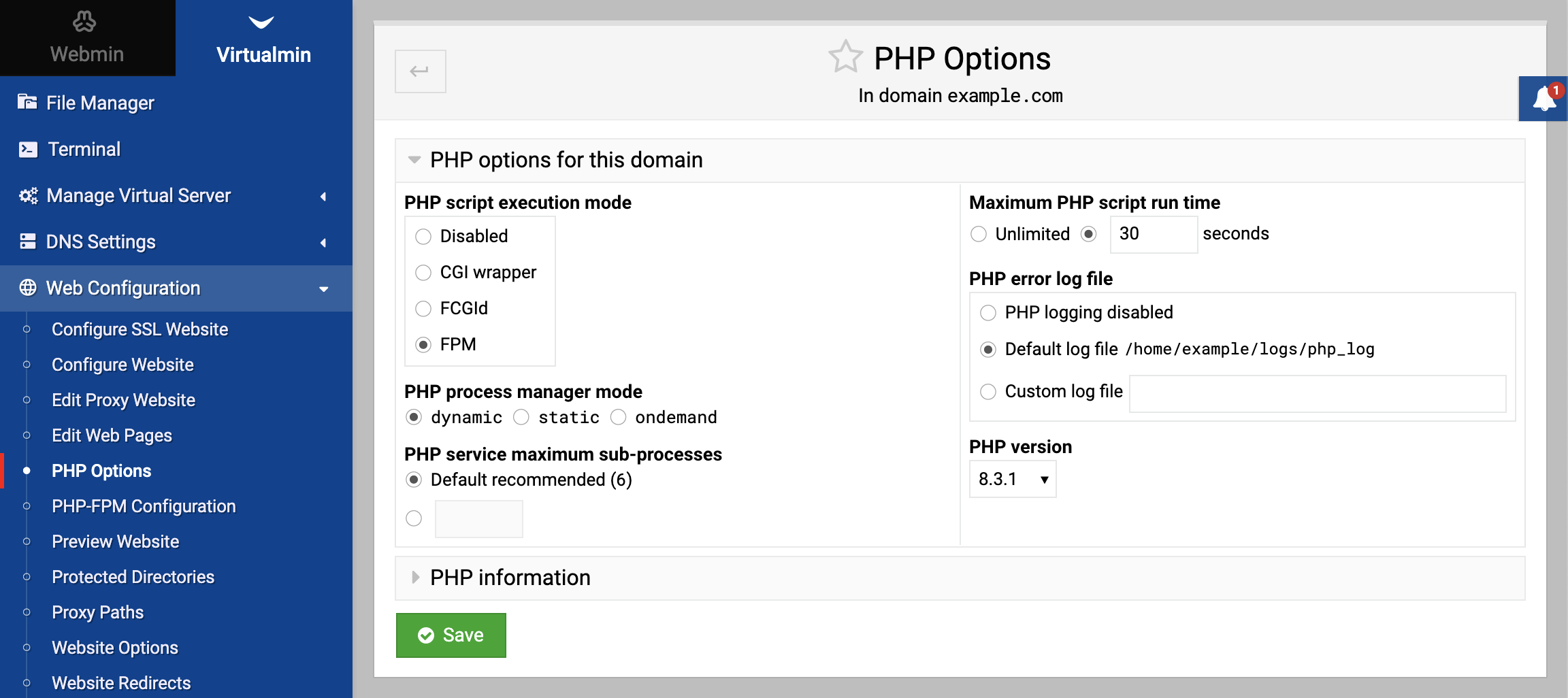
Virtualmin offers a robust application deployment stack for PHP, supporting multiple PHP versions. The recommended and default execution mode for PHP is PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager), which provides improved performance, stability, and resource management for PHP applications.
PHP execution modes
Virtualmin configures PHP applications to execute with user-level isolation by utilizing FPM (PHP-FPM) and FCGId/CGI wrapper (suEXEC) execution modes:
This architecture replaces the need for mod_php. PHP-FPM allows for PHP scripts to run as long-lived processes, which significantly reduces overhead and improves performance, bringing it on par with the speed of mod_php while maintaining a high level of security.
Recommended PHP execution mode
PHP-FPM is recommended for executing PHP scripts due to its improved isolation, which provides separate process pools for each website, enhancing security in shared hosting environments. It offers superior performance and scalability, efficiently handling high loads and dynamically adjusting resources to match website demands. PHP-FPM’s advanced features include adaptive process spawning and emergency restarts, alongside flexible configuration options for resource limits and PHP settings on a per-website basis. It is compatible with both Apache and Nginx webservers, adding to its versatility, and its ease of use is augmented by Virtualmin, which simplifies its setup and management.
Precautions regarding mod_php
When managing multiple PHP versions in Virtualmin, it’s crucial to understand the implications of installing mod_php:
Avoid
mod_php: This Apache module embeds PHP directly into the server. It poses significant security risks, especially in shared environments.mod_phpdoesn’t isolate scripts between different sites, potentially allowing one site to affect others on the same server.Identifying
mod_phpinstallation- In Debian and derivatives,
mod_phpis typically part of packages likelibapache2-mod-php(or other version numbers likelibapache2-mod-php8.3). - In EL systems, look for packages named
php,php83-phpor similar, depending on the PHP version.
- In Debian and derivatives,
Uninstalling mod_php
To remove mod_php and avoid numerous issues, you can uninstall it using your package manager.
- For Debian and derivatives
apt-get remove libapache2-mod-php* - For EL systems
dnf remove $(dnf list installed | awk -F. '{print $1}' | grep -E '^php$|^php[0-9]+-php$')
After uninstallation, restart Apache to apply the changes.
Individual PHP configuration
A significant advantage of running PHP in either PHP-FPM or FCGId/CGI wrapper execution mode is that it allows each virtual server to have its unique configuration. This setup provides the flexibility to customize the PHP environment according to the specific requirements of individual applications.
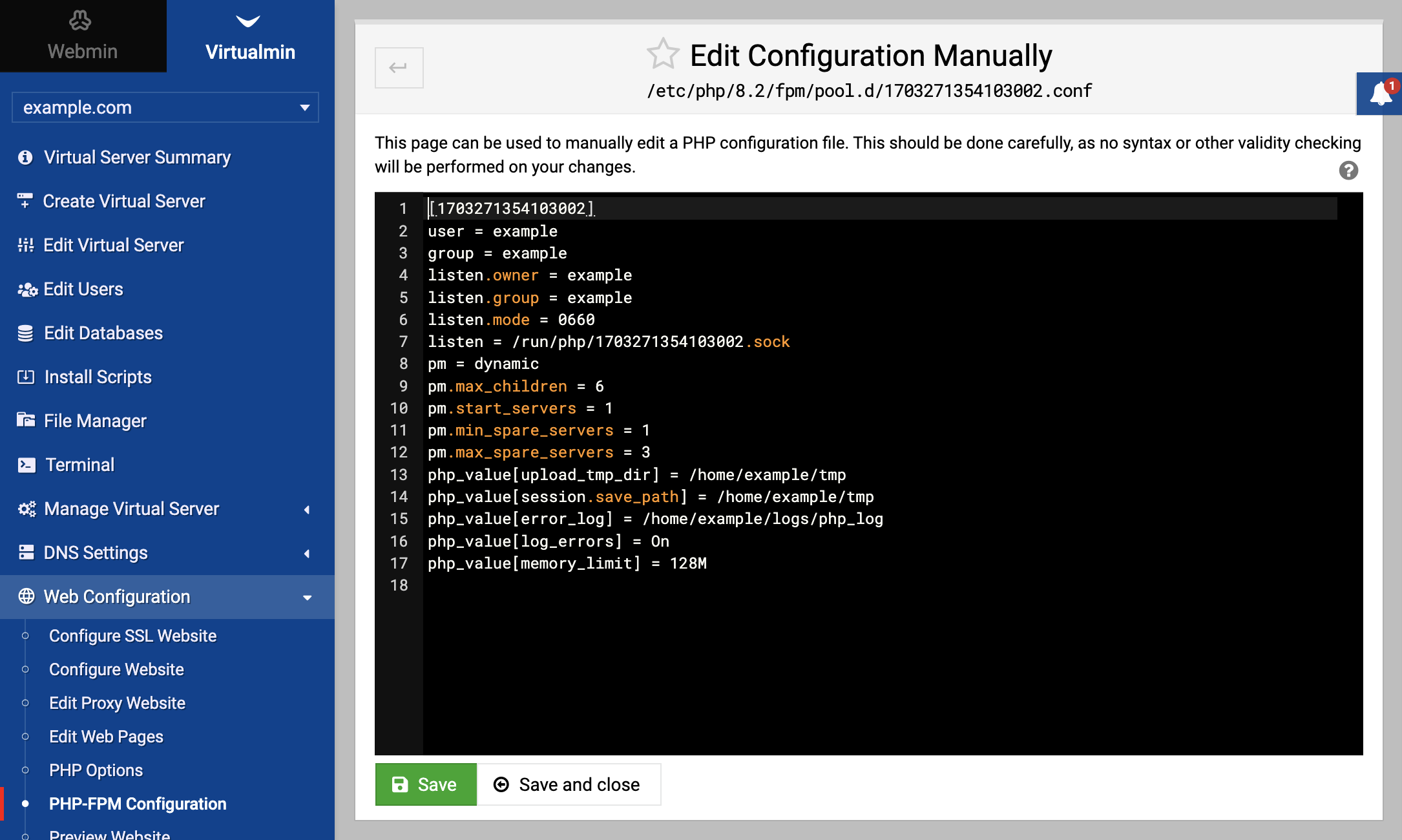
For PHP-FPM, individual pool configurations for virtual servers are typically found in the /etc/php-fpm.d directory. These pools are specific to the PHP-FPM mode and facilitate the management of different PHP configurations for each virtual server separately.
On the other hand, in FCGId/CGI wrapper modes, the php.ini files, which are located under virtual server home, i.e. in the ~/etc/php directory, allow for distinct PHP configurations.
These settings can either be adjusted under the Web Configuration menu for each domain and even can be directly modified using a text editor:
Note:
Changes to the system-wide /etc/php.ini will not affect the php.ini of individual virtual servers. To make system-wide changes, you may consider using the /etc/php.d directory, where files are automatically included by PHP. Adding a new .ini file in this directory with your directives can propagate changes across all PHP versions.
Updating PHP configurations
Updates to PHP configurations across multiple virtual servers can be done using mass update feature from List Virtual Servers page (available only in Virtualmin Professional) or using Virtualmin CLI.
For example, to increase the memory_limit for all domains to 256M, the following command can be executed:
virtualmin modify-php-ini --all-domains --ini-name memory_limit --ini-value 256M
Default PHP version
When creating new virtual servers, you can choose a default PHP execution mode and version by adjusting the server template settings in System Settings ⇾ Server Templates ⇾ PHP Options page.
For deprecated versions such as PHP 7.4, it is highly recommended to upgrade to a supported version to ensure the security and performance of your PHP applications.